Haseung Jun
Annika Tekumulla
Haseung Jun
Annika Tekumulla
Skills you’ll gain in this topic:
- Describe the stages of the cell cycle, including interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis.
- Explain how cells ensure accurate DNA replication and division.
- Relate the cell cycle to growth, development, and tissue repair.
- Illustrate the importance of checkpoints in regulating cell division.
- Predict the effects of cell cycle disruptions on organismal health.
Phases and Functions of the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is the sequence of steps prior to cell division. Cell division is crucial to survival because it replaces bad cells, and plays a role in growth and tissue repair. Mitosis (the process of cell division) is an asexual reproduction, which means the parent cell will produce two identical daughter cells that are also identical to the parent cell. This does not bring diversity within the cells, but it is an efficient way to create cells that will replace old cells.
In eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is highly regulated through the growth and reproduction of cells. If this process is not regulated, the cell will continue to divide non-stop, which is what a cancer cell is. Therefore, there are checkpoints and signals to regulate the cell cycle throughout each phase. Depending on the cell type, the cell division can happen frequently or nearly never. The cell cycle consists of 5 phases: interphase (G1, S, and G2), mitosis, and cytokinesis.
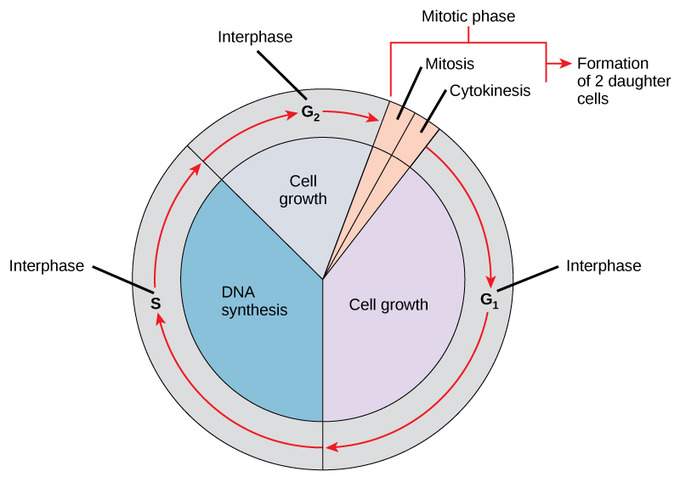
Image courtesy of Bio LibreTexts.
Interphase
Interphase contains the phases G1, S, and G2. Over 90% of the cell cycle is spent in interphase! During interphase, the chromatin of the cell is threadlike so when looking at a cell undergoing interphase, a centrosome can be spotted with 2 centrioles. During the S phase, the centrosome is duplicated.
Now, let’s break down the phases.
- 1️⃣ G1 is a period of intense growth and activity.
- 2️⃣ S is used to stand for the synthesis of DNA. The DNA is replicated so the cell now has two sets of the same DNA.
- 3️⃣ G2, the cell continues to grow in order to finish cell division.
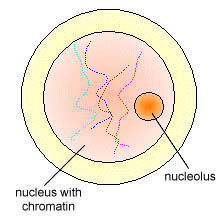
Image courtesy of Doc Kaiser's Microbiology.
Keep in mind, a cell can go into the G0 phase, which is a phase where a cell never divides. These G0 phase cells can reenter the cell cycle when they receive appropriate signals, and dividing cells can exit the cell cycle at any given time. Because the cell cycle is highly regulated, cells are only told to divide when it receives a growth factor via the signal-response pathway.
Mitosis can also be contagious, because a currently-mitosis-cell can activate mitosis in another cell nearby. Mammalian cells are able to sense cells around it and tell others to divide and stop dividing when there are enough cells.
Mitosis
Mitosis is the part of the cell cycle when the nucleus of the cell is divided. Even though mitosis is one process, it is broken down into prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- Prophase is the first phase of mitosis. In prophase, the nuclear membrane begins to disintegrate, chromosomes condense, and the spindle begins to form. Because DNA is a bunch of tangled mess, the DNA is nicely wrapped into chromosomes so equal dividing will become a little easier.
- During metaphase, chromosomes begin to line up in the middle of the cell. Also, the centrosomes move to the ends of the cell.
- Anaphase is when the centromeres finally separate. The spindle pulls apart the now sister chromosomes (identical copies).
- Telophase begins when the chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell. The chromosomes begin to uncoil and return to their threadlike shape. Mitosis is complete once the cell separates and 2 separate nucleoli form.
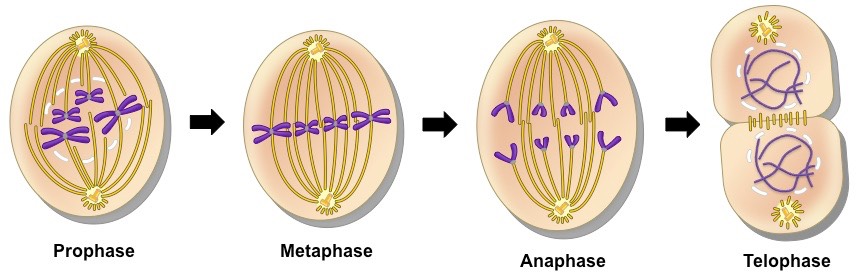
Image courtesy of BioNinja.
Cytokinesis
The process of cytokinesis is different in plant and animal cells. After mitosis occurs, cytokinesis begins. Cytokinesis is when the cytoplasm is divided.
The process of cytokinesis is different in plant and animal cells.
- For plant cells, a cell plate made of stiff sugars is formed and surrounds the cell membrane. In plant cells, the daughter cells do not separate from each other. Instead, a new cell wall is created.
- For animal cells, a cleavage furrow is formed. A cleavage furrow is a groove that is created in the middle of the cell surface. The cytoplasm then begins to separate.
<< Hide Menu
Haseung Jun
Annika Tekumulla
Haseung Jun
Annika Tekumulla
Skills you’ll gain in this topic:
- Describe the stages of the cell cycle, including interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis.
- Explain how cells ensure accurate DNA replication and division.
- Relate the cell cycle to growth, development, and tissue repair.
- Illustrate the importance of checkpoints in regulating cell division.
- Predict the effects of cell cycle disruptions on organismal health.
Phases and Functions of the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is the sequence of steps prior to cell division. Cell division is crucial to survival because it replaces bad cells, and plays a role in growth and tissue repair. Mitosis (the process of cell division) is an asexual reproduction, which means the parent cell will produce two identical daughter cells that are also identical to the parent cell. This does not bring diversity within the cells, but it is an efficient way to create cells that will replace old cells.
In eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is highly regulated through the growth and reproduction of cells. If this process is not regulated, the cell will continue to divide non-stop, which is what a cancer cell is. Therefore, there are checkpoints and signals to regulate the cell cycle throughout each phase. Depending on the cell type, the cell division can happen frequently or nearly never. The cell cycle consists of 5 phases: interphase (G1, S, and G2), mitosis, and cytokinesis.

Image courtesy of Bio LibreTexts.
Interphase
Interphase contains the phases G1, S, and G2. Over 90% of the cell cycle is spent in interphase! During interphase, the chromatin of the cell is threadlike so when looking at a cell undergoing interphase, a centrosome can be spotted with 2 centrioles. During the S phase, the centrosome is duplicated.
Now, let’s break down the phases.
- 1️⃣ G1 is a period of intense growth and activity.
- 2️⃣ S is used to stand for the synthesis of DNA. The DNA is replicated so the cell now has two sets of the same DNA.
- 3️⃣ G2, the cell continues to grow in order to finish cell division.

Image courtesy of Doc Kaiser's Microbiology.
Keep in mind, a cell can go into the G0 phase, which is a phase where a cell never divides. These G0 phase cells can reenter the cell cycle when they receive appropriate signals, and dividing cells can exit the cell cycle at any given time. Because the cell cycle is highly regulated, cells are only told to divide when it receives a growth factor via the signal-response pathway.
Mitosis can also be contagious, because a currently-mitosis-cell can activate mitosis in another cell nearby. Mammalian cells are able to sense cells around it and tell others to divide and stop dividing when there are enough cells.
Mitosis
Mitosis is the part of the cell cycle when the nucleus of the cell is divided. Even though mitosis is one process, it is broken down into prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- Prophase is the first phase of mitosis. In prophase, the nuclear membrane begins to disintegrate, chromosomes condense, and the spindle begins to form. Because DNA is a bunch of tangled mess, the DNA is nicely wrapped into chromosomes so equal dividing will become a little easier.
- During metaphase, chromosomes begin to line up in the middle of the cell. Also, the centrosomes move to the ends of the cell.
- Anaphase is when the centromeres finally separate. The spindle pulls apart the now sister chromosomes (identical copies).
- Telophase begins when the chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell. The chromosomes begin to uncoil and return to their threadlike shape. Mitosis is complete once the cell separates and 2 separate nucleoli form.

Image courtesy of BioNinja.
Cytokinesis
The process of cytokinesis is different in plant and animal cells. After mitosis occurs, cytokinesis begins. Cytokinesis is when the cytoplasm is divided.
The process of cytokinesis is different in plant and animal cells.
- For plant cells, a cell plate made of stiff sugars is formed and surrounds the cell membrane. In plant cells, the daughter cells do not separate from each other. Instead, a new cell wall is created.
- For animal cells, a cleavage furrow is formed. A cleavage furrow is a groove that is created in the middle of the cell surface. The cytoplasm then begins to separate.

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.