Jed Quiaoit
Samantha Himegarner
Jed Quiaoit
Samantha Himegarner
Skills you’ll gain in this topic:
- Explain how environmental changes drive continued evolution in species.
- Describe examples of ongoing evolutionary change in populations today.
- Predict evolutionary shifts based on current environmental and genetic pressures.
- Analyze case studies showing adaptation and genetic variation in real-time.
- Relate continuous evolution to the resilience and adaptability of species.
Genomic Changes
Another good reasoning for the theory of evolution is that there is evidence in every species, not just a select few. There has been proven genomic changes over time, which helps assume the influence of a shared common ancestor. As fossils are found and dated, scientists have also noticed continuous change in their characteristics and the fossil record in general.
Natural Selection
Most notably, however, is the constant adaptation of bacteria in their ability to resist antibiotics. This works as its own form of malicious natural selection. When a new antibiotic is developed and dispersed, the bacteria that are unaffected (usually due to a random mutation) will reproduce and pass along that mutation (as the genetic code is identical), and soon the antibiotic will be rendered useless in killing off the harmful bacteria.
Image courtesy of Giphy.
Evolution is constant in this never-ending cycle, along with that of pesticides, herbicides, and even chemotherapy drugs. Even worse, pathogens will continue to evolve and cause emergent diseases that were once eradicated.
Populations
Recall the big idea behind evolution in a population level:
Populations of organisms evolve over time through the process of natural selection. This process acts on the genetic variation present within a population, and can lead to the development of new traits and adaptations that increase the chances of survival and reproduction for the individuals that possess them. Over many generations, these small changes can accumulate, leading to the evolution of new species. 👑
Ways Populations Evolved
All species have evolved and continue to evolve in various ways, such as: 👇
Genomic changes over time: The genetic makeup of a population can change over time through various processes, including mutation, recombination, and genetic drift. These changes can lead to the development of new traits or the loss of existing ones, and can ultimately result in the evolution of new species.
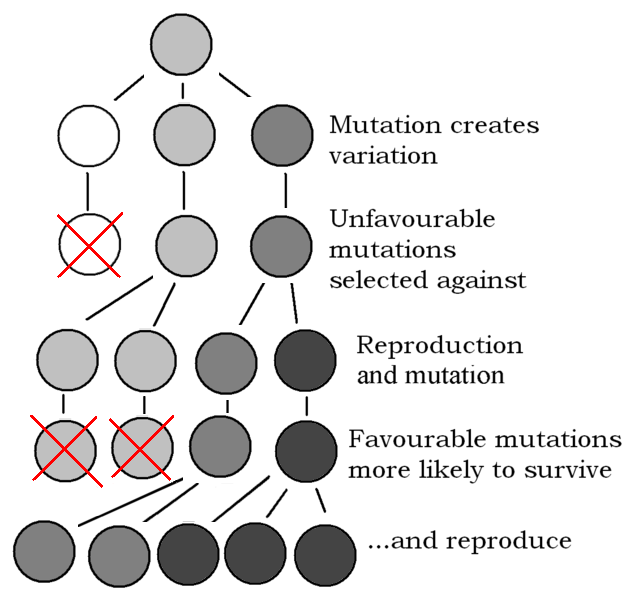
Source: IMGBin
Continuous change in the fossil record: The fossil record provides evidence of the evolution of life on Earth over millions of years. Fossils of extinct organisms from different geologic periods reveal that the forms and structures of living things have changed over time, and that many species that once existed are now extinct.
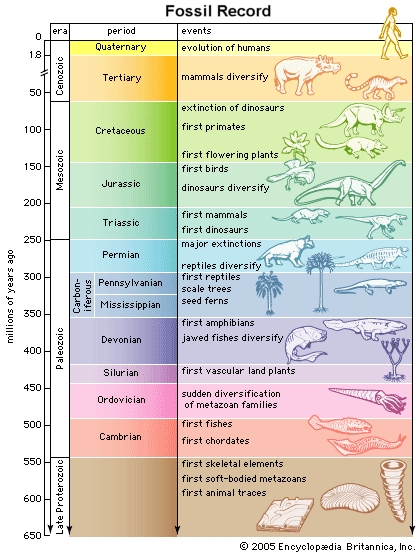
Source: ThingLink
Evolution of resistance to antibiotics, pesticides, herbicides, or chemotherapy drugs: When organisms are exposed to these agents, a small number of individuals may have genetic variations that allow them to survive. These individuals reproduce and pass on their resistant traits to their offspring, leading to the evolution of resistance in the population. This is becoming a growing concern in modern medicine.
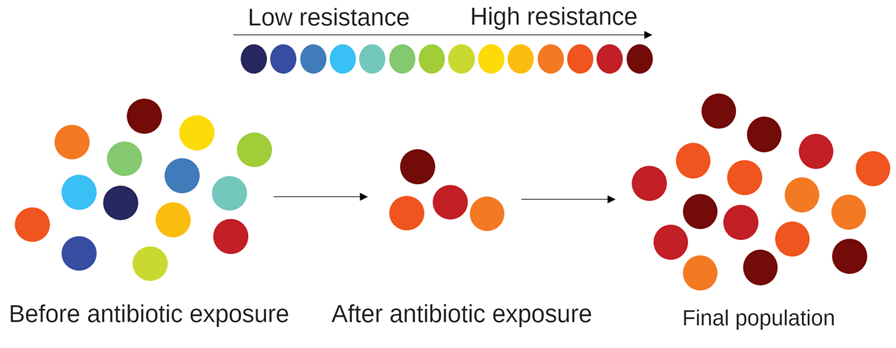
Source: BiteScis
Pathogens evolve and cause emergent diseases: Pathogens, such as viruses and bacteria, can also evolve over time. This process can lead to the emergence of new diseases or the reemergence of previously controlled diseases. For example, the current COVID-19 pandemic is caused by a novel strain of the coronavirus that emerged in 2019. The virus has continued to evolve, leading to multiple variants that are more transmissible and potentially more virulent.
In summary, evolution is a continuous process that occurs in all living organisms, and it is driven by genetic variation, natural selection, and other mechanisms. Over time, these mechanisms can lead to the development of new species, the emergence of new diseases, and other significant changes in the living world! 🌎
Check out the AP Bio Unit 7 Replays or watch the 2021 Unit 7 Cram
<< Hide Menu
Jed Quiaoit
Samantha Himegarner
Jed Quiaoit
Samantha Himegarner
Skills you’ll gain in this topic:
- Explain how environmental changes drive continued evolution in species.
- Describe examples of ongoing evolutionary change in populations today.
- Predict evolutionary shifts based on current environmental and genetic pressures.
- Analyze case studies showing adaptation and genetic variation in real-time.
- Relate continuous evolution to the resilience and adaptability of species.
Genomic Changes
Another good reasoning for the theory of evolution is that there is evidence in every species, not just a select few. There has been proven genomic changes over time, which helps assume the influence of a shared common ancestor. As fossils are found and dated, scientists have also noticed continuous change in their characteristics and the fossil record in general.
Natural Selection
Most notably, however, is the constant adaptation of bacteria in their ability to resist antibiotics. This works as its own form of malicious natural selection. When a new antibiotic is developed and dispersed, the bacteria that are unaffected (usually due to a random mutation) will reproduce and pass along that mutation (as the genetic code is identical), and soon the antibiotic will be rendered useless in killing off the harmful bacteria.

Image courtesy of Giphy.
Evolution is constant in this never-ending cycle, along with that of pesticides, herbicides, and even chemotherapy drugs. Even worse, pathogens will continue to evolve and cause emergent diseases that were once eradicated.
Populations
Recall the big idea behind evolution in a population level:
Populations of organisms evolve over time through the process of natural selection. This process acts on the genetic variation present within a population, and can lead to the development of new traits and adaptations that increase the chances of survival and reproduction for the individuals that possess them. Over many generations, these small changes can accumulate, leading to the evolution of new species. 👑
Ways Populations Evolved
All species have evolved and continue to evolve in various ways, such as: 👇
Genomic changes over time: The genetic makeup of a population can change over time through various processes, including mutation, recombination, and genetic drift. These changes can lead to the development of new traits or the loss of existing ones, and can ultimately result in the evolution of new species.

Source: IMGBin
Continuous change in the fossil record: The fossil record provides evidence of the evolution of life on Earth over millions of years. Fossils of extinct organisms from different geologic periods reveal that the forms and structures of living things have changed over time, and that many species that once existed are now extinct.

Source: ThingLink
Evolution of resistance to antibiotics, pesticides, herbicides, or chemotherapy drugs: When organisms are exposed to these agents, a small number of individuals may have genetic variations that allow them to survive. These individuals reproduce and pass on their resistant traits to their offspring, leading to the evolution of resistance in the population. This is becoming a growing concern in modern medicine.

Source: BiteScis
Pathogens evolve and cause emergent diseases: Pathogens, such as viruses and bacteria, can also evolve over time. This process can lead to the emergence of new diseases or the reemergence of previously controlled diseases. For example, the current COVID-19 pandemic is caused by a novel strain of the coronavirus that emerged in 2019. The virus has continued to evolve, leading to multiple variants that are more transmissible and potentially more virulent.
In summary, evolution is a continuous process that occurs in all living organisms, and it is driven by genetic variation, natural selection, and other mechanisms. Over time, these mechanisms can lead to the development of new species, the emergence of new diseases, and other significant changes in the living world! 🌎
Check out the AP Bio Unit 7 Replays or watch the 2021 Unit 7 Cram

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.