Browse By Unit
Subject
🧪AP Chemistry
Study Guides by Unit
⚛️Unit 1 – Atomic Structure and Properties
🤓Unit 2 – Molecular and Ionic Bonding
🌀Unit 3 – Intermolecular Forces and Properties
🧪Unit 4 – Chemical Reactions
👟Unit 5 – Kinetics
🔥Unit 6 – Thermochemistry
⚖️Unit 7 – Equilibrium
🍊Unit 8 – Acids and Bases
🔋Unit 9 – Applications of Thermodynamics
What are ionic solids?
1 min read•july 11, 2024
Ionic solids are one of the four major types of solids you need to know about in AP chemistry. The others are metallic, covalent network, and molecular solids. Want more info? Check out this video replay that covers the 🎥 structures of solids for AP chem.
The Basics ⚛️
- Ionic solids are made up of oppositely charged ions held together by electrostatic attraction (a.k.a. ionic bonds).
- Electrostatic attraction just describes the attractive force between a positive charge and a negative charge.
- The ions form a crystal lattice structure, seen in NaCl below:
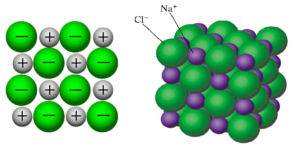
Source: Redefining Knowledge
Properties
- They're hard and brittle.
- They have high melting points because ionic bonds require a lot of energy to break.
- In solid form, ionic compounds are poor conductors.
- When melted or dissolved in water, they will conduct electricity because they dissociate into individual ions that are free to move around.
- Not all ionic compounds are soluble, though, so keep those solubility rules in mind! - If you need a review, check out this study guide for solubility.
<< Hide Menu
What are ionic solids?
1 min read•july 11, 2024
Ionic solids are one of the four major types of solids you need to know about in AP chemistry. The others are metallic, covalent network, and molecular solids. Want more info? Check out this video replay that covers the 🎥 structures of solids for AP chem.
The Basics ⚛️
- Ionic solids are made up of oppositely charged ions held together by electrostatic attraction (a.k.a. ionic bonds).
- Electrostatic attraction just describes the attractive force between a positive charge and a negative charge.
- The ions form a crystal lattice structure, seen in NaCl below:

Source: Redefining Knowledge
Properties
- They're hard and brittle.
- They have high melting points because ionic bonds require a lot of energy to break.
- In solid form, ionic compounds are poor conductors.
- When melted or dissolved in water, they will conduct electricity because they dissociate into individual ions that are free to move around.
- Not all ionic compounds are soluble, though, so keep those solubility rules in mind! - If you need a review, check out this study guide for solubility.

© 2025 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.