Browse By Unit
3.11 Spectroscopy and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
5 min read•june 18, 2024
Kanya Shah
Dalia Savy
Kanya Shah
Dalia Savy
What Is Light?
Scientists began to understand light and the way light works by analyzing the light that was emitted or absorbed by substances. 💡
The light we see with our eyes👀, visible light, is one type of electromagnetic radiation; because electromagnetic radiation carries through space, it is also known as radiant energy.
Light is carried in the form of photons, a type of quantum particle that acts as a "force-carrying particle" for electromagnetic energy. For example, when you turn on a flashlight🔦, trillions of photons shoot out, creating a beam of light that illuminates a dark area. The same concept is applied in lasers and in many incredibly important measurements involving concentrations of solutions, as we'll see later in this unit when discussing the Beer-Lambert law.
😲Fun fact! The word LASER is actually an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation ⚡
We'll get a deeper understanding of what light really is and its role in the quantum world in the next study guide and key concept!
Properties of Light
When we discuss light, we typically refer to its wavelength and its frequency. These two terms can help us describe how light will act. Light is an interesting quantum idea because of the fact that it acts both as a particle (the photon) and as a wave. This is called particle-wave duality. This goes back to what we discussed in unit one and electrons also exist as both particles and waves.
When thinking of a wave, it is useful to visualize it as a sine wave, oscillating back and forth periodically.
- Amplitude refers to the vertical height of the wave from the midline. The amplitude of a wave determines the light's intensity or brightness. The greater the amplitude, the brighter the light.
- Wavelength (λ) refers to the length of one period of the wave. This can be described either as the peak-to-peak distance, or the zero-to-zero distance. It is typically measured in nanometers (nm), but it can also be measured in meters or micrometers. The wavelength of a wave determines the color of light.
- Frequency(ν) describes the number of waves that pass a fixed place in a given amount of time and is measured in cycles per second (s^-1) or Hertz (Hz). The hertz is defined as one cycle per second. The frequency of a wave is directly proportional to the speed at which the wave is traveling. Basically, the faster the wave, the greater the frequency. Frequency and wavelength have an inverse relationship. Essentially, a high wavelength implies a small frequency and vice versa. This relationship can be expressed through the equation c = λν, where c refers to the speed of light. We'll come back to this formula in the next section!
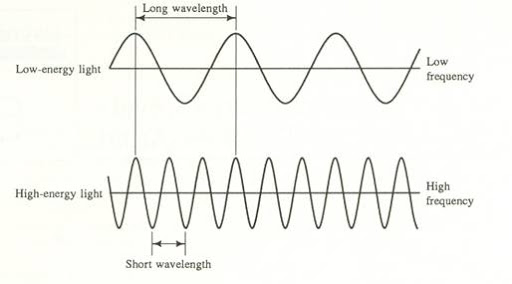
Image Courtesy of Florida State College
The Electromagnetic Spectrum🌈
Visible light, which is the light we can see, is only a small category of light. The electromagnetic spectrum includes all wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, ranging from very short gamma rays to very long radio waves. A key trend to note is that electromagnetic radiation can be characterized by its wavelength; the shorter the wavelength, the higher the frequency.
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction of radiant energy and matter. The electromagnetic spectrum diagram is shown below to use as a reference:
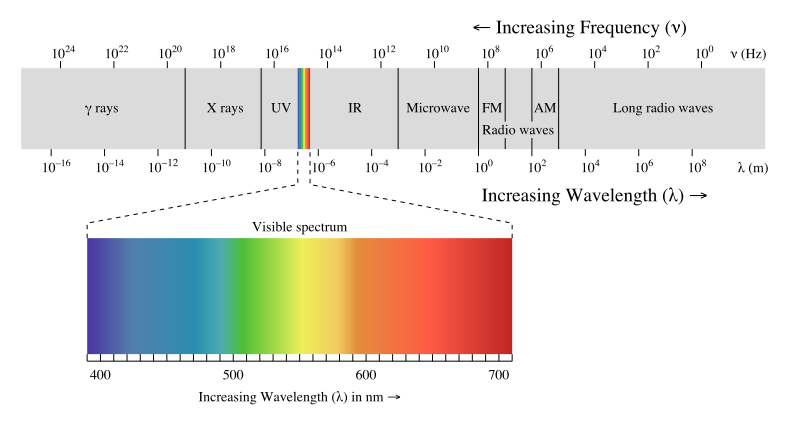
Image Courtesy of Khan Academy
There are a few things to notice about the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum, so let's break it down:
- It is broken up into sections based on wavelength from ten-thousandths of nanometers long to hundreds of meters long. To put this in perspective, a nanometer is one billionth of a meter or 10^-9 meters.
- If we start on the left of the EM spectrum, we can see gamma (γ) rays have the shortest wavelength and thus the highest frequency. Because of their high frequencies, they can ionize radiation and are very dangerous. This means that they have enough energy to ionize atoms or molecules by removing their electrons and can easily pass through matter. This makes them very dangerous to humans and we are only exposed to them in small amounts in medical and industrial settings.
- Next on the EM spectrum is X-rays, something you're already familiar with! X-rays have a longer wavelength and lower frequency when compared to gamma rays. Their properties allow them to pass through substances that block visible light, which allows us to use them to image internal bones and organs!
- Next, we got ultraviolet radiation or UV rays. Since their frequency is still relatively high (although low compared to gamma and x-rays), they are very harmful to us in high doses. UV rays are the reason why we have to wear sunscreen when exposed to sunlight for a prolonged period of time, as excessive exposure to UV light increases the risk of skin cancer.
- Taking a look at the EM spectrum, we can see that next is the visible light spectrum, which is the EM radiation that we can see. The photoreceptors in our eyes are only receptive to light within this spectrum, ranging from 400 nm in wavelength to 700 nm. Note that purple💜 has the shortest wavelength while red❤️ has the longest wavelength.- UV rays and visible light are both associated with transitions in energy levels at an atomic level.
- After the visible light spectrum, we have infrared radiation, represented as IR on the EM spectrum above. All of the heat that we feel is infrared radiation since warm objects (even human bodies) emit light at this wavelength! IR is also associated with transitions in molecular vibrational levels.
- Moving towards the opposite end of the spectrum, we are now at microwaves. Microwaves are associated with transitions in molecular rotational levels. They are used in satellite systems and can cook food (hence our microwaves in the kitchen!).- How do microwave ovens warm our food? When you microwave food, the microwaves pass through the container and into the food. The microwaves are absorbed by the food, causing the molecules to vibrate and produce heat.
- Last but not least, we have radio waves. Radio waves have the longest wavelength and thus the lowest frequency. Because of this, radio waves are not really dangerous to us. They are actually used to transmit signals responsible for radio, our cell signal, and television! Here is another image that quickly summarizes the practical use of these different rays of light.
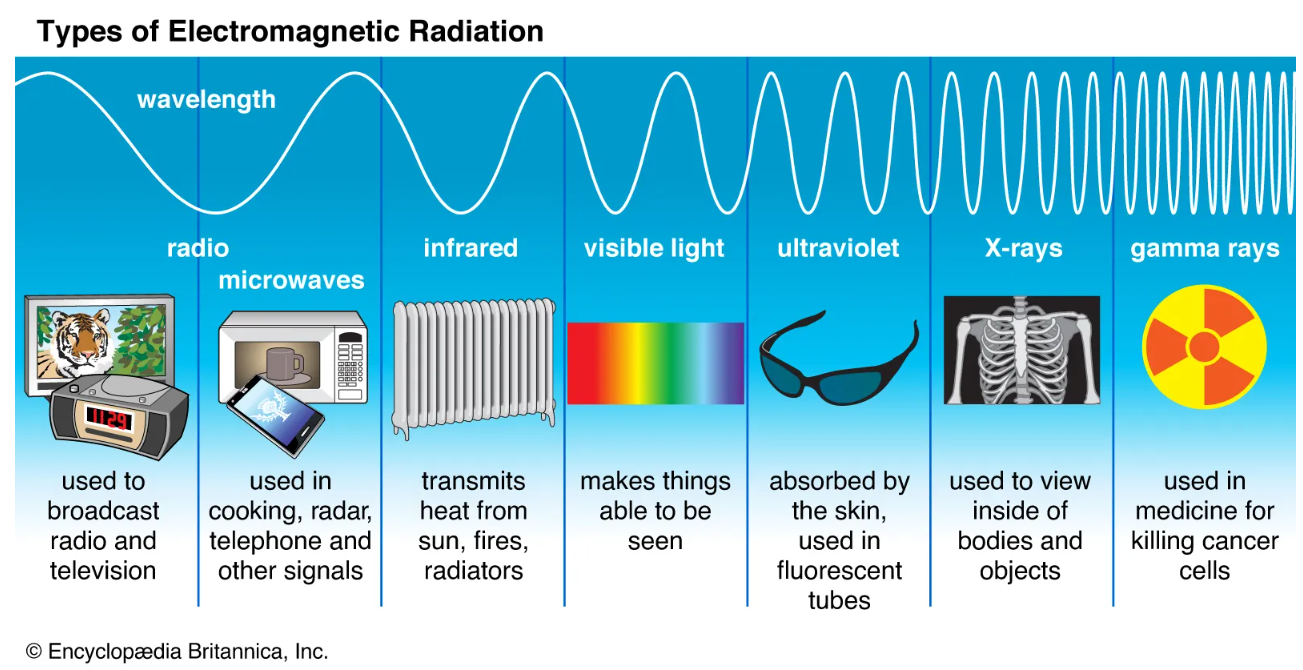
Image Courtesy of Britannica
<< Hide Menu
3.11 Spectroscopy and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
5 min read•june 18, 2024
Kanya Shah
Dalia Savy
Kanya Shah
Dalia Savy
What Is Light?
Scientists began to understand light and the way light works by analyzing the light that was emitted or absorbed by substances. 💡
The light we see with our eyes👀, visible light, is one type of electromagnetic radiation; because electromagnetic radiation carries through space, it is also known as radiant energy.
Light is carried in the form of photons, a type of quantum particle that acts as a "force-carrying particle" for electromagnetic energy. For example, when you turn on a flashlight🔦, trillions of photons shoot out, creating a beam of light that illuminates a dark area. The same concept is applied in lasers and in many incredibly important measurements involving concentrations of solutions, as we'll see later in this unit when discussing the Beer-Lambert law.
😲Fun fact! The word LASER is actually an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation ⚡
We'll get a deeper understanding of what light really is and its role in the quantum world in the next study guide and key concept!
Properties of Light
When we discuss light, we typically refer to its wavelength and its frequency. These two terms can help us describe how light will act. Light is an interesting quantum idea because of the fact that it acts both as a particle (the photon) and as a wave. This is called particle-wave duality. This goes back to what we discussed in unit one and electrons also exist as both particles and waves.
When thinking of a wave, it is useful to visualize it as a sine wave, oscillating back and forth periodically.
- Amplitude refers to the vertical height of the wave from the midline. The amplitude of a wave determines the light's intensity or brightness. The greater the amplitude, the brighter the light.
- Wavelength (λ) refers to the length of one period of the wave. This can be described either as the peak-to-peak distance, or the zero-to-zero distance. It is typically measured in nanometers (nm), but it can also be measured in meters or micrometers. The wavelength of a wave determines the color of light.
- Frequency(ν) describes the number of waves that pass a fixed place in a given amount of time and is measured in cycles per second (s^-1) or Hertz (Hz). The hertz is defined as one cycle per second. The frequency of a wave is directly proportional to the speed at which the wave is traveling. Basically, the faster the wave, the greater the frequency. Frequency and wavelength have an inverse relationship. Essentially, a high wavelength implies a small frequency and vice versa. This relationship can be expressed through the equation c = λν, where c refers to the speed of light. We'll come back to this formula in the next section!

Image Courtesy of Florida State College
The Electromagnetic Spectrum🌈
Visible light, which is the light we can see, is only a small category of light. The electromagnetic spectrum includes all wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, ranging from very short gamma rays to very long radio waves. A key trend to note is that electromagnetic radiation can be characterized by its wavelength; the shorter the wavelength, the higher the frequency.
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction of radiant energy and matter. The electromagnetic spectrum diagram is shown below to use as a reference:

Image Courtesy of Khan Academy
There are a few things to notice about the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum, so let's break it down:
- It is broken up into sections based on wavelength from ten-thousandths of nanometers long to hundreds of meters long. To put this in perspective, a nanometer is one billionth of a meter or 10^-9 meters.
- If we start on the left of the EM spectrum, we can see gamma (γ) rays have the shortest wavelength and thus the highest frequency. Because of their high frequencies, they can ionize radiation and are very dangerous. This means that they have enough energy to ionize atoms or molecules by removing their electrons and can easily pass through matter. This makes them very dangerous to humans and we are only exposed to them in small amounts in medical and industrial settings.
- Next on the EM spectrum is X-rays, something you're already familiar with! X-rays have a longer wavelength and lower frequency when compared to gamma rays. Their properties allow them to pass through substances that block visible light, which allows us to use them to image internal bones and organs!
- Next, we got ultraviolet radiation or UV rays. Since their frequency is still relatively high (although low compared to gamma and x-rays), they are very harmful to us in high doses. UV rays are the reason why we have to wear sunscreen when exposed to sunlight for a prolonged period of time, as excessive exposure to UV light increases the risk of skin cancer.
- Taking a look at the EM spectrum, we can see that next is the visible light spectrum, which is the EM radiation that we can see. The photoreceptors in our eyes are only receptive to light within this spectrum, ranging from 400 nm in wavelength to 700 nm. Note that purple💜 has the shortest wavelength while red❤️ has the longest wavelength.- UV rays and visible light are both associated with transitions in energy levels at an atomic level.
- After the visible light spectrum, we have infrared radiation, represented as IR on the EM spectrum above. All of the heat that we feel is infrared radiation since warm objects (even human bodies) emit light at this wavelength! IR is also associated with transitions in molecular vibrational levels.
- Moving towards the opposite end of the spectrum, we are now at microwaves. Microwaves are associated with transitions in molecular rotational levels. They are used in satellite systems and can cook food (hence our microwaves in the kitchen!).- How do microwave ovens warm our food? When you microwave food, the microwaves pass through the container and into the food. The microwaves are absorbed by the food, causing the molecules to vibrate and produce heat.
- Last but not least, we have radio waves. Radio waves have the longest wavelength and thus the lowest frequency. Because of this, radio waves are not really dangerous to us. They are actually used to transmit signals responsible for radio, our cell signal, and television! Here is another image that quickly summarizes the practical use of these different rays of light.

Image Courtesy of Britannica

© 2025 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.