Jeanne Stansak
dylan_black_2025
Jeanne Stansak
dylan_black_2025
What is a Monopsony?
The second type of factor (resource) market is called a monopsony. A monopsony is an imperfectly competitive factor market where only a single firm buys resources. More broadly, it is any market which has one buyer and many sellers. For example, imagine a town where there was only one employer: a coal mining company. There are many workers supplying labor to the company, but the company is the only firm that is buying, meaning they have market power and as such can have some control over the wage.
Characteristics of Monopsonies
-
- One, large firm hires all workers in a single labor market and is large enough to control the labor market - this is the definition of a monopsony
-
- The market is imperfectly competitive - this means that it does not fit our previous assumptions of a perfectly competitive labor market
-
- The firm is a wage maker - because the firm is the only firm demanding labor, they have control over the price in the market. This means they will minimize wage at the lowest possible willingness to sell
-
- MRC > Supply (willingness to sell) - This is because when you hire an additional worker, you must pay them a higher wage than the previous worker. However, you cannot wage discriminate, so you not only have the additional cost of that worker, but also the cost of bringing all the earlier workers up to the current wage rate. This is analogous to MR < D for a monopoly
-
- The firm will hire the quantity of labor where MRP = MRC - this is the profit maximizing principle for factor markets
-
- The firm will pay workers a wage that they are willing and able to work for below their MRP - this is because of market power
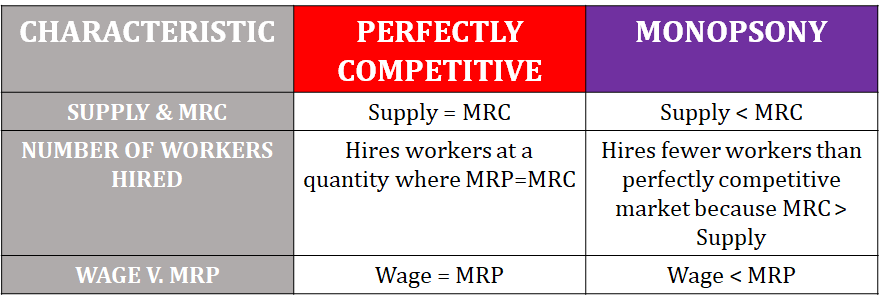
Differences between a Perfectly Competitive Labor Market and a Monopsony
Graphing a Monoposony
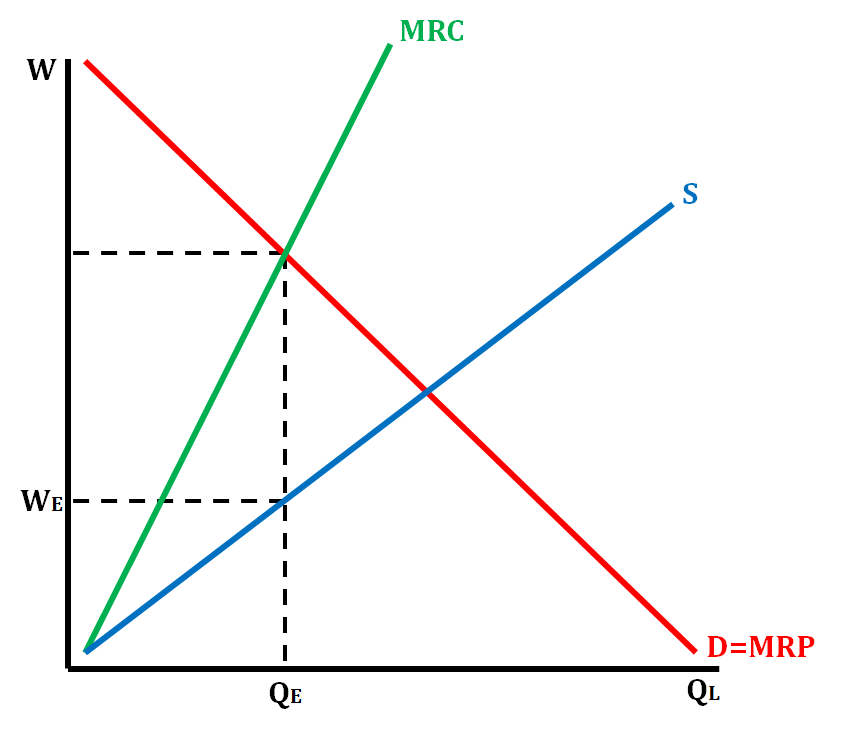
Demand = MRP is the same as in perfect competition, and is because of the law of diminishing marginal returns. A firm is only willing to demand labor at MRP (since they want all the revenue possible), so D = MRP.
MRC > S in a monopsony because the firm cannot wage discriminate. All workers must be paid the same, so each additional worker leads to an increase in wage higher than the lowest willingness. This is analogous to our reasoning as to why MR < D for a monopoly.
In a monopsony, we determine the number of workers by finding where MRP = MRC and then going down to the horizontal axis. We determine wage by finding MRP = MRC and then going down to the supply curve and over to the vertical axis. This is because the firm will charge the lowest wage the worker is willing to be paid for, which is defined by labor supply curve.
AP Micro 2011B Problem 3
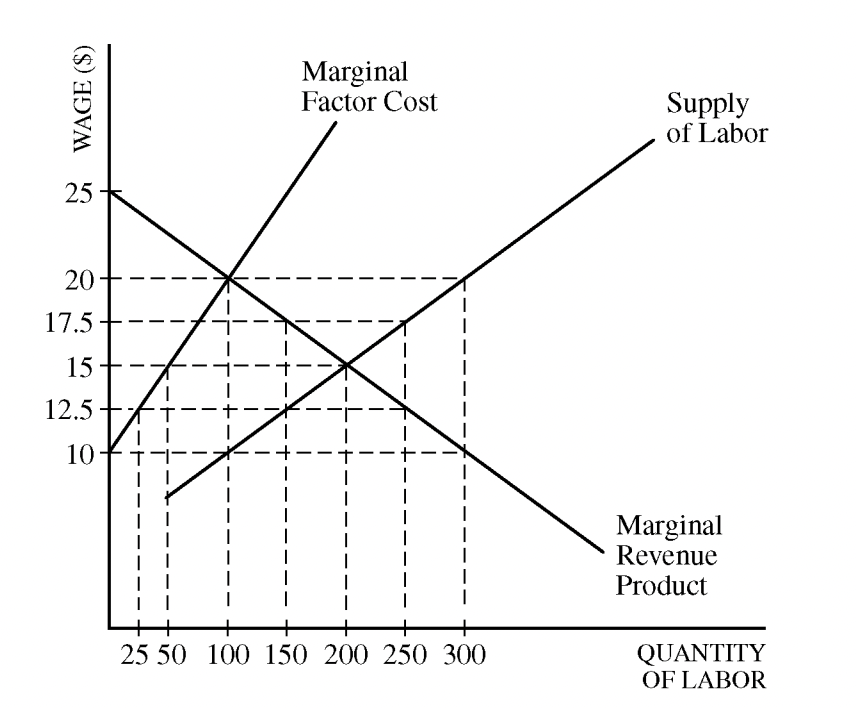
Woodland is a small town in which everyone works for TreeMart, the local lumber company. TreeMart is a monopsonist in the labor market and a perfect competitor in the lumber market. In the short run, labor is the only variable input. The labor market for TreeMart is given in the graph above.
a) Identify the profit-maximizing quantity of labor for TreeMart
b) Identify the wage rate TreeMart pays to hire the profit-maximizing quantity of labor
c) Identify the quantity of labor hired in each of the following scenarios:
i) TreeMart operates in a competitive labor market
ii) The government imposes a minimum wage of $12.50. Explain
Answer and Explanation
a) TreeMart will hire where MRP = MRC. This is at QL = 100.
b) At QL = 100, we go down to the lowest willingness to sell, which is w = 10
c i) In a competitive market, MRC = S, so we hire where S = MRP, which is a quantity of 200 units.
c ii) A minimum wage is a wage minimum, which is a price floor. Thus, MRC = $12.50, so Q = 150. After Q = 150, the wage would be higher, but until then, the supply curve is horizontal.
<< Hide Menu
Jeanne Stansak
dylan_black_2025
Jeanne Stansak
dylan_black_2025
What is a Monopsony?
The second type of factor (resource) market is called a monopsony. A monopsony is an imperfectly competitive factor market where only a single firm buys resources. More broadly, it is any market which has one buyer and many sellers. For example, imagine a town where there was only one employer: a coal mining company. There are many workers supplying labor to the company, but the company is the only firm that is buying, meaning they have market power and as such can have some control over the wage.
Characteristics of Monopsonies
-
- One, large firm hires all workers in a single labor market and is large enough to control the labor market - this is the definition of a monopsony
-
- The market is imperfectly competitive - this means that it does not fit our previous assumptions of a perfectly competitive labor market
-
- The firm is a wage maker - because the firm is the only firm demanding labor, they have control over the price in the market. This means they will minimize wage at the lowest possible willingness to sell
-
- MRC > Supply (willingness to sell) - This is because when you hire an additional worker, you must pay them a higher wage than the previous worker. However, you cannot wage discriminate, so you not only have the additional cost of that worker, but also the cost of bringing all the earlier workers up to the current wage rate. This is analogous to MR < D for a monopoly
-
- The firm will hire the quantity of labor where MRP = MRC - this is the profit maximizing principle for factor markets
-
- The firm will pay workers a wage that they are willing and able to work for below their MRP - this is because of market power
Differences between a Perfectly Competitive Labor Market and a Monopsony

Graphing a Monoposony

Demand = MRP is the same as in perfect competition, and is because of the law of diminishing marginal returns. A firm is only willing to demand labor at MRP (since they want all the revenue possible), so D = MRP.
MRC > S in a monopsony because the firm cannot wage discriminate. All workers must be paid the same, so each additional worker leads to an increase in wage higher than the lowest willingness. This is analogous to our reasoning as to why MR < D for a monopoly.
In a monopsony, we determine the number of workers by finding where MRP = MRC and then going down to the horizontal axis. We determine wage by finding MRP = MRC and then going down to the supply curve and over to the vertical axis. This is because the firm will charge the lowest wage the worker is willing to be paid for, which is defined by labor supply curve.
AP Micro 2011B Problem 3

Woodland is a small town in which everyone works for TreeMart, the local lumber company. TreeMart is a monopsonist in the labor market and a perfect competitor in the lumber market. In the short run, labor is the only variable input. The labor market for TreeMart is given in the graph above.
a) Identify the profit-maximizing quantity of labor for TreeMart
b) Identify the wage rate TreeMart pays to hire the profit-maximizing quantity of labor
c) Identify the quantity of labor hired in each of the following scenarios:
i) TreeMart operates in a competitive labor market
ii) The government imposes a minimum wage of $12.50. Explain
Answer and Explanation
a) TreeMart will hire where MRP = MRC. This is at QL = 100.
b) At QL = 100, we go down to the lowest willingness to sell, which is w = 10
c i) In a competitive market, MRC = S, so we hire where S = MRP, which is a quantity of 200 units.
c ii) A minimum wage is a wage minimum, which is a price floor. Thus, MRC = $12.50, so Q = 150. After Q = 150, the wage would be higher, but until then, the supply curve is horizontal.

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.