Browse By Unit
Unit 8 Overview: The Postwar Period & Cold War (1945-1980)
7 min read•june 18, 2024
Dalia Savy
Eric Leiden
Dalia Savy
Eric Leiden
Summary of Period 8 Events
Following World War II, the United States was the strongest military and economic power in the world. ☝
The economy exploded through the 1960s with suburbs and Baby Boomers. Cold War tension with the Soviet Union heated up, with incidents occurring all over the world. Civil Rights issues✊🏾dominated the 1950s and 60s. The 1970s saw America suffer a crisis in confidence as oil shortages and a hostage crisis shook the nation’s confidence. Ronald Reagan became the president in 1980, representing a monumental change in Cold War diplomacy.
About 10-17% of the AP U.S. History examination is going to cover material from this unit. You got this!
Post-War America
Levittown suburbs sprouted all across the US, especially in the blossoming sunbelt, leading to the baby boom👰👪. Returning vets settled down for a simple life, capitalizing on the GI Bill to help finance college tuition and low-interest home loans.
“Keeping up with the Joneses” kept the department stores in business and televisions brought news and sitcoms into living rooms. For many, it appeared to be “the good life” 👌
Cold War
The good life was shrouded by the perpetual fear of a nuclear war. Tensions with the Soviet Union ran high as the Iron Curtain descended upon Eastern Europe.
The Truman Plan, Eisenhower Doctrine, and NATO attempted to contain communism prior to 1960.
- The Truman Doctrine, announced by President Harry Truman in 1947, was a policy of providing military and economic assistance to countries threatened by communist expansion. The doctrine, which stated that the United States would provide aid to any country threatened by communism, was a response to the perceived threat of Soviet expansion in Europe and the Middle East.
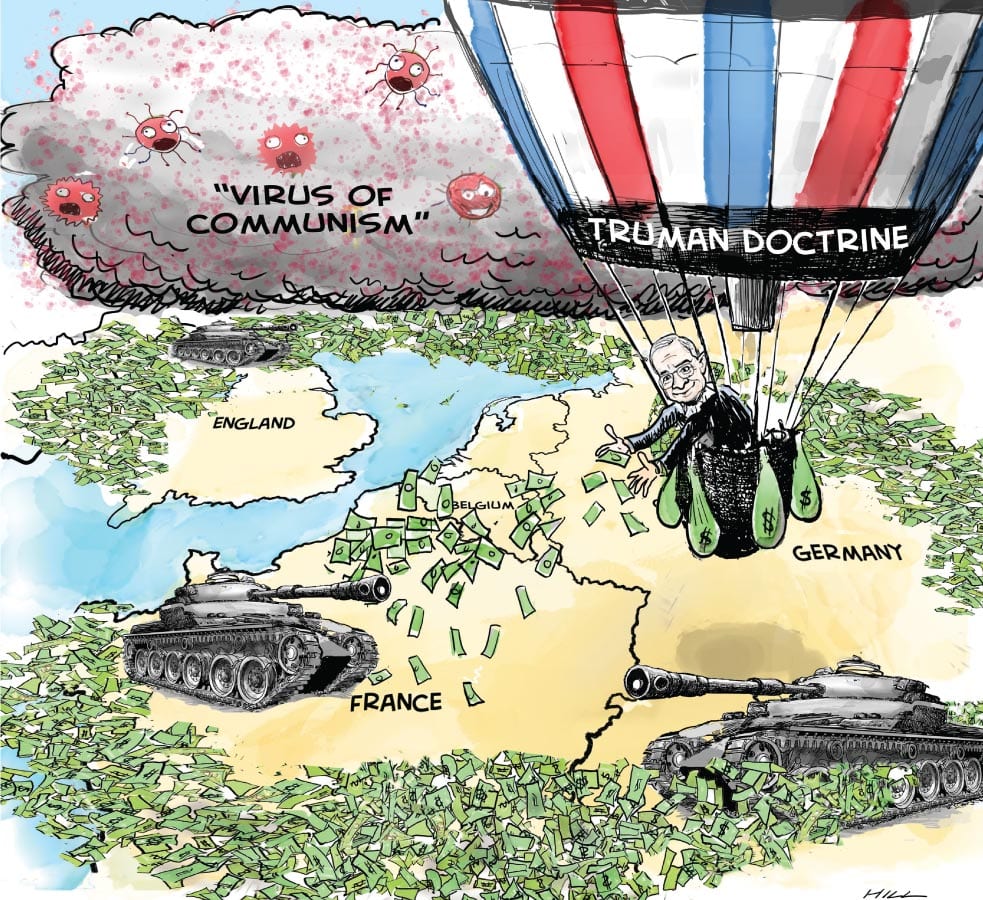
Image Courtesy of Apprend.io
- The Eisenhower Doctrine, announced by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1957, was a policy of providing military and economic assistance to countries in the Middle East to contain Soviet expansion in that region. The doctrine stated that the United States would provide aid and, if necessary, military intervention to any Middle Eastern country threatened by communism or armed aggression from another country.
- NATO, which was established in 1949, was a military alliance of Western countries that was created to counter the military threat from the Soviet Union and its allies. The alliance was intended to provide a collective defense against any potential Soviet aggression in Europe and to contain the spread of communism in the region. Events like the Korean War abroad and McCarthyism back home kept most people on edge. Alger Hiss and the Rosenbergs had people believing there were communists on every block. Joseph McCarthy’s accusations caused widespread panic and pitted neighbor against neighbor. He led a highly publicized campaign to root out supposed communist influence in the U.S. government, military, and society at large.
The Second Red Scare had arrived...it was a period of increased fear of communist infiltration and subversion in the United States. It's actually also known as the McCarthy Era, named after Senator Joseph McCarthy.
Eisenhower’s Diplomacy
Eisenhower’s policy rested on the idea of Massive Retaliation. This strategy held that if the Soviet Union or any other hostile nation used nuclear weapons against the United States or its allies, the United States would respond with a massive nuclear strike.
Relying on John Foster Dulles’, Eisenhower instituted his New Look foreign policy. Covert operations by the CIA took place in the Middle East and Asia. However, the launching of Sputnik 🚀by the Soviets challenges America’s academic superiority, and the U-2 ✈️ event leaves Americans second-guessing their Commander in Chief.

Image Courtesy of Digital Humanities at A-State
JFK’s New Frontier
President Kennedy swaggers into the Whitehouse ready to combat communism through his Flexible Response. The strategy of Flexible Response held that the United States should maintain a range of military options, including conventional and nuclear forces, in order to deter and respond to aggression by the Soviet Union and other potential adversaries. The goal of this strategy was to provide the United States with the flexibility to respond to a wide range of threats, rather than relying solely on the threat of massive nuclear retaliation.
Unfortunately, the Bay of Pigs 🐖 is a huge fiasco and the building of the Berlin Wall is a slap in the face. Incredibly, Kennedy redeems his diplomatic reputation with his skillful handling of the Cuban Missile Crisis 🚢
Johnson and Vietnam
Although Johnson inherited “advisors” in Vietnam, he supersized America’s presence there following the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution. Johnson escalated the war and misinformation created a Credibility Gap, dampening the communication between President Johnson and his people. The TET Offensive 💥 shakes people’s confidence in the war, and anti-war demonstrators call for bringing the troops home.
Nixon’s Detente
Nixon immediately begins the process of Vietnamization to turn the conflict in Vietnam over to the South Vietnamese, trying to end U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War.
Nixon and Kissinger also used diplomacy to try to end the war. One of the key events was the "Ping Pong Diplomacy" in which the U.S. table tennis team visited China in 1971. This was the first time Americans had been to China since the communist revolution in 1949, and it helped to ease tensions between the two countries. The talks between the U.S. and China also helped to relieve tension with the Soviet Union as the two communist nations were rivals and had a strained relationship.
However, news of the My Lai massacre, Kent State Shootings, and Pentagon papers serve to shadow the otherwise positive foreign diplomacy. Ultimately, the Watergate Scandal seals Nixon’s fate in history 👎

Image Courtesy of CBS News
Carter’s Foreign Policy
Carter may have excelled in human rights diplomacy and negotiating the Camp David Accords, but he is remembered for his failure to return the Hostages from Iran. In addition, the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan smothers any positive achievements.
Civil Rights and Black America
Following WWII, Jackie Robinson ⚾ breaks the color barrier in baseball while young, black children learn in segregated schools. Judge Warren issues the verdict in Brown v. Board of Education**,** requiring schools to desegregate with all deliberate speed. As a result, schools take their time and Little Rock, Arkansas becomes a showdown as nine Black students are escorted by troops to their classes.
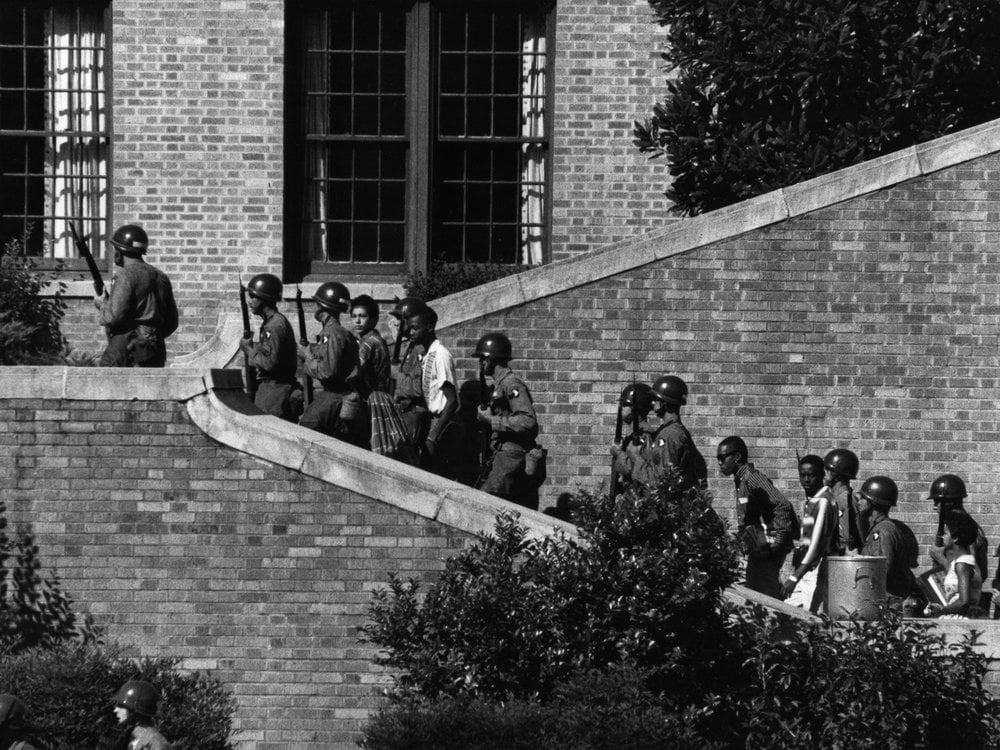

The Little Rock Nine; Image Courtesy of the Smithsonian Magazine
Southern Resistance
The Southern Manifesto encourages the blocking of integration at the local level. Meanwhile, the SCLC, CORE, and SNCC begin to peacefully challenge the notion in Montgomery, Selma, and Birmingham. Violent attacks on the peaceful protestors caught on film in Birmingham spur a call to reform by President Kennedy. Martin Luther King, Jr. plans his March on Washington to demand stronger civil rights legislation.
Johnson’s Great Society
Kennedy’s assassination opens the door for Johnson’s liberal social reform package. Welfare programs, Medicare, and Medicaid provide much-needed benefits to many struggling Americans. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 provide more protections for minorities in society and at the polling booth. Further decisions such as Miranda v. Arizona by the Warren Court create further protections for those under arrest 🔗
Social Revolutionaries
The political protests spawn a new group of young people rebelling against societal norms. Experimenting with drugs and a sexual revolution challenge traditional values. Hippies protest the war, and Woodstock becomes a musical sensation featuring artists such as Jimi Hendrix 🎸and Janis Joplin 🎤
Social Movements
Women-led movements by Betty Friedan and her Feminine Mystique defy the Cult of Domesticity by insisting upon equal opportunity in the workplace. The Gay and Lesbian Movement 🏳️🌈gains speed following the incident at the Stonewall Inn. Hispanic America sees gains under the leadership of Cesar Chavez, and the American Indian Movement stages fish-ins while demanding increased tribal rights and economic opportunity.
Main Events
1945: End of World War II
1947: Truman Doctrine
1949: NATO created
1950: Korean War
1952: Eisenhower Elected
1954: Brown vs. Board of Education
1955: Montgomery Bus Boycott
1957: Little Rock Nine / Sputnik launched
1960: Kennedy Elected
1962: Cuban Missile Crisis
1963: Birmingham Riots / Kennedy Assassinated / Johnson President
1964: Civil Rights Act
1965: Voting Rights Act
1968: Martin Luther King, Jr. and Robert Kennedy Assassinated / TET offensive
1968: Nixon Elected
1973: Roe vs. Wade
1974: Nixon Resigns
1976: Carter Elected
1979: Iranian Hostage Crisis begins
1980: Reagan Elected
Major Themes
- The United States will take a front-seat position in global leadership in creating a stable world following World War II.
- Efforts to expand the government will result in far-reaching social and political changes following World War II.
- Post-war societal and economic changes will lead to two decades of prosperity.
- Civil Rights Reform is demanded following World War II and resulted in massive progress toward equality.
- Cold War tensions spark economic, educational, and societal change as competition with the Soviets leads to massive changes.
- Tensions from within are manifested in massive riots and protests as people battle political, social, and economic inequalities.
- Trust in government is compromised by misleading politicians and scandals leading to a crisis in the confidence of our political leaders.
How to Study Unit 8
We suggest making sure to create a study plan and set up your study space with a good environment. Make sure to have a good grasp on the key timeline and know your historical figures! To help with your productivity, especially during the last few days before the exam, you should use a Pomodoro study timer to break up your sessions into intervals and make time for breaks. It is also hugely beneficial to study with friends so that you can motivate one another and crush the APUSH exam together! 🙌🏾
<< Hide Menu
Unit 8 Overview: The Postwar Period & Cold War (1945-1980)
7 min read•june 18, 2024
Dalia Savy
Eric Leiden
Dalia Savy
Eric Leiden
Summary of Period 8 Events
Following World War II, the United States was the strongest military and economic power in the world. ☝
The economy exploded through the 1960s with suburbs and Baby Boomers. Cold War tension with the Soviet Union heated up, with incidents occurring all over the world. Civil Rights issues✊🏾dominated the 1950s and 60s. The 1970s saw America suffer a crisis in confidence as oil shortages and a hostage crisis shook the nation’s confidence. Ronald Reagan became the president in 1980, representing a monumental change in Cold War diplomacy.
About 10-17% of the AP U.S. History examination is going to cover material from this unit. You got this!
Post-War America
Levittown suburbs sprouted all across the US, especially in the blossoming sunbelt, leading to the baby boom👰👪. Returning vets settled down for a simple life, capitalizing on the GI Bill to help finance college tuition and low-interest home loans.
“Keeping up with the Joneses” kept the department stores in business and televisions brought news and sitcoms into living rooms. For many, it appeared to be “the good life” 👌
Cold War
The good life was shrouded by the perpetual fear of a nuclear war. Tensions with the Soviet Union ran high as the Iron Curtain descended upon Eastern Europe.
The Truman Plan, Eisenhower Doctrine, and NATO attempted to contain communism prior to 1960.
- The Truman Doctrine, announced by President Harry Truman in 1947, was a policy of providing military and economic assistance to countries threatened by communist expansion. The doctrine, which stated that the United States would provide aid to any country threatened by communism, was a response to the perceived threat of Soviet expansion in Europe and the Middle East.

Image Courtesy of Apprend.io
- The Eisenhower Doctrine, announced by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1957, was a policy of providing military and economic assistance to countries in the Middle East to contain Soviet expansion in that region. The doctrine stated that the United States would provide aid and, if necessary, military intervention to any Middle Eastern country threatened by communism or armed aggression from another country.
- NATO, which was established in 1949, was a military alliance of Western countries that was created to counter the military threat from the Soviet Union and its allies. The alliance was intended to provide a collective defense against any potential Soviet aggression in Europe and to contain the spread of communism in the region. Events like the Korean War abroad and McCarthyism back home kept most people on edge. Alger Hiss and the Rosenbergs had people believing there were communists on every block. Joseph McCarthy’s accusations caused widespread panic and pitted neighbor against neighbor. He led a highly publicized campaign to root out supposed communist influence in the U.S. government, military, and society at large.
The Second Red Scare had arrived...it was a period of increased fear of communist infiltration and subversion in the United States. It's actually also known as the McCarthy Era, named after Senator Joseph McCarthy.
Eisenhower’s Diplomacy
Eisenhower’s policy rested on the idea of Massive Retaliation. This strategy held that if the Soviet Union or any other hostile nation used nuclear weapons against the United States or its allies, the United States would respond with a massive nuclear strike.
Relying on John Foster Dulles’, Eisenhower instituted his New Look foreign policy. Covert operations by the CIA took place in the Middle East and Asia. However, the launching of Sputnik 🚀by the Soviets challenges America’s academic superiority, and the U-2 ✈️ event leaves Americans second-guessing their Commander in Chief.

Image Courtesy of Digital Humanities at A-State
JFK’s New Frontier
President Kennedy swaggers into the Whitehouse ready to combat communism through his Flexible Response. The strategy of Flexible Response held that the United States should maintain a range of military options, including conventional and nuclear forces, in order to deter and respond to aggression by the Soviet Union and other potential adversaries. The goal of this strategy was to provide the United States with the flexibility to respond to a wide range of threats, rather than relying solely on the threat of massive nuclear retaliation.
Unfortunately, the Bay of Pigs 🐖 is a huge fiasco and the building of the Berlin Wall is a slap in the face. Incredibly, Kennedy redeems his diplomatic reputation with his skillful handling of the Cuban Missile Crisis 🚢
Johnson and Vietnam
Although Johnson inherited “advisors” in Vietnam, he supersized America’s presence there following the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution. Johnson escalated the war and misinformation created a Credibility Gap, dampening the communication between President Johnson and his people. The TET Offensive 💥 shakes people’s confidence in the war, and anti-war demonstrators call for bringing the troops home.
Nixon’s Detente
Nixon immediately begins the process of Vietnamization to turn the conflict in Vietnam over to the South Vietnamese, trying to end U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War.
Nixon and Kissinger also used diplomacy to try to end the war. One of the key events was the "Ping Pong Diplomacy" in which the U.S. table tennis team visited China in 1971. This was the first time Americans had been to China since the communist revolution in 1949, and it helped to ease tensions between the two countries. The talks between the U.S. and China also helped to relieve tension with the Soviet Union as the two communist nations were rivals and had a strained relationship.
However, news of the My Lai massacre, Kent State Shootings, and Pentagon papers serve to shadow the otherwise positive foreign diplomacy. Ultimately, the Watergate Scandal seals Nixon’s fate in history 👎

Image Courtesy of CBS News
Carter’s Foreign Policy
Carter may have excelled in human rights diplomacy and negotiating the Camp David Accords, but he is remembered for his failure to return the Hostages from Iran. In addition, the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan smothers any positive achievements.
Civil Rights and Black America
Following WWII, Jackie Robinson ⚾ breaks the color barrier in baseball while young, black children learn in segregated schools. Judge Warren issues the verdict in Brown v. Board of Education**,** requiring schools to desegregate with all deliberate speed. As a result, schools take their time and Little Rock, Arkansas becomes a showdown as nine Black students are escorted by troops to their classes.

The Little Rock Nine; Image Courtesy of the Smithsonian Magazine
Southern Resistance
The Southern Manifesto encourages the blocking of integration at the local level. Meanwhile, the SCLC, CORE, and SNCC begin to peacefully challenge the notion in Montgomery, Selma, and Birmingham. Violent attacks on the peaceful protestors caught on film in Birmingham spur a call to reform by President Kennedy. Martin Luther King, Jr. plans his March on Washington to demand stronger civil rights legislation.
Johnson’s Great Society
Kennedy’s assassination opens the door for Johnson’s liberal social reform package. Welfare programs, Medicare, and Medicaid provide much-needed benefits to many struggling Americans. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 provide more protections for minorities in society and at the polling booth. Further decisions such as Miranda v. Arizona by the Warren Court create further protections for those under arrest 🔗
Social Revolutionaries
The political protests spawn a new group of young people rebelling against societal norms. Experimenting with drugs and a sexual revolution challenge traditional values. Hippies protest the war, and Woodstock becomes a musical sensation featuring artists such as Jimi Hendrix 🎸and Janis Joplin 🎤
Social Movements
Women-led movements by Betty Friedan and her Feminine Mystique defy the Cult of Domesticity by insisting upon equal opportunity in the workplace. The Gay and Lesbian Movement 🏳️🌈gains speed following the incident at the Stonewall Inn. Hispanic America sees gains under the leadership of Cesar Chavez, and the American Indian Movement stages fish-ins while demanding increased tribal rights and economic opportunity.
Main Events
1945: End of World War II
1947: Truman Doctrine
1949: NATO created
1950: Korean War
1952: Eisenhower Elected
1954: Brown vs. Board of Education
1955: Montgomery Bus Boycott
1957: Little Rock Nine / Sputnik launched
1960: Kennedy Elected
1962: Cuban Missile Crisis
1963: Birmingham Riots / Kennedy Assassinated / Johnson President
1964: Civil Rights Act
1965: Voting Rights Act
1968: Martin Luther King, Jr. and Robert Kennedy Assassinated / TET offensive
1968: Nixon Elected
1973: Roe vs. Wade
1974: Nixon Resigns
1976: Carter Elected
1979: Iranian Hostage Crisis begins
1980: Reagan Elected
Major Themes
- The United States will take a front-seat position in global leadership in creating a stable world following World War II.
- Efforts to expand the government will result in far-reaching social and political changes following World War II.
- Post-war societal and economic changes will lead to two decades of prosperity.
- Civil Rights Reform is demanded following World War II and resulted in massive progress toward equality.
- Cold War tensions spark economic, educational, and societal change as competition with the Soviets leads to massive changes.
- Tensions from within are manifested in massive riots and protests as people battle political, social, and economic inequalities.
- Trust in government is compromised by misleading politicians and scandals leading to a crisis in the confidence of our political leaders.
How to Study Unit 8
We suggest making sure to create a study plan and set up your study space with a good environment. Make sure to have a good grasp on the key timeline and know your historical figures! To help with your productivity, especially during the last few days before the exam, you should use a Pomodoro study timer to break up your sessions into intervals and make time for breaks. It is also hugely beneficial to study with friends so that you can motivate one another and crush the APUSH exam together! 🙌🏾

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.